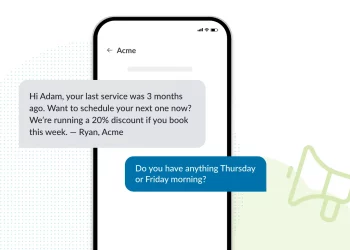
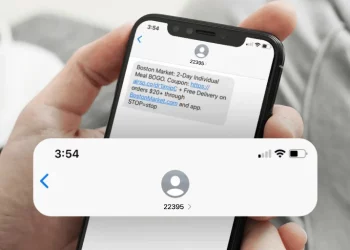
Text messaging has become integral to our communication landscape, facilitating quick and convenient conversations. However, with the rise of technology, new challenges have emerged, including text spoofing. Text spoofing refers to falsifying the sender’s information to deceive the recipient.
In this article, we will delve into the concept of text spoofing, explore its implications, and discuss the potential risks associated with spoofed text messages. Understanding text spoofing is crucial for individuals and businesses to safeguard their privacy, security, and trust in the digital realm.
Understanding Text Spoofing
Text spoofing involves manipulating the information displayed on a recipient’s device to make it appear like a message originated from a different sender. This technique is commonly used in phishing scams, fraudulent activities, or malicious attempts to deceive or trick individuals. Text spoofing can occur through various methods, such as using specialized software, online platforms, or exploiting vulnerabilities in the telecommunications system.
Implications of Text Spoofing
Identity Theft and Fraud:
Text spoofing enables fraudsters to impersonate individuals, organizations, or service providers, leading to identity theft and fraudulent activities. They may deceive recipients into sharing personal information, financial details, or login credentials under pretenses, resulting in potential financial loss or compromised accounts.
Social Engineering Attacks:
Text spoofing is often employed in social engineering attacks, where scammers manipulate emotions or exploit a sense of urgency to trick recipients into acting against their best interests. This can involve clicking malicious links, downloading harmful attachments, or revealing sensitive information.
Damage to Reputations:
Text spoofing can harm the reputation of legitimate individuals or organizations whose identities are spoofed. If recipients fall victim to spoofed messages and associate the deception with the falsely represented entity, it can lead to reputational damage and a loss of trust.
Security Breaches and Malware Distribution:
Spoofed text messages may contain links or attachments that, when interacted with, can lead to security breaches or malware distribution. These malicious elements can compromise devices, steal personal data, or provide unauthorized access to sensitive systems.
Legal Consequences:
Text spoofing is illegal in many jurisdictions, and perpetrators can face legal consequences if caught. Law enforcement agencies actively pursue cases of text spoofing, aiming to protect individuals and businesses from fraudulent activities and maintain the integrity of digital communications.
Preventing Text Spoofing and Protecting Yourself
Exercise Caution:
Be skeptical of unsolicited messages, especially those requesting personal information or financial details. Verify the sender’s identity through a trusted source or contact the supposed sender directly using verified contact information.
Implement Security Measures:
Utilize security software and keep your devices and applications current. This can help detect and mitigate potential threats associated with spoofed text messages.
Educate Yourself:
Stay informed about common scams and techniques used in text spoofing. Familiarize yourself with the warning signs, such as grammatical errors, suspicious URLs, or requests for sensitive information.
Report Suspicious Activities:
If you receive a spoofed text message or suspect fraudulent activity, report it to your mobile service provider, local authorities, or appropriate governing bodies. Reporting helps raise awareness, prevent further incidents, and potentially assist investigations.
Caller ID Spoofing:
Text spoofing often involves caller ID spoofing, where scammers manipulate the caller identification information displayed on a recipient’s device. This can make the message appear to originate from a trusted source or a recognizable phone number, increasing the likelihood of the recipient falling victim to the scam.
Smishing Attacks:
Smishing, a combination of SMS and phishing, is a form of text spoofing that aims to trick recipients into revealing personal information or taking malicious actions. Scammers may send spoofed text messages pretending to be a legitimate organization, such as a bank, requesting account details, passwords, or payment information.
Business Impersonation:
Text spoofing can also target businesses, with scammers posing as company representatives to deceive customers or employees. These spoofed messages may request sensitive information or instruct recipients to perform fraudulent actions, such as transferring funds to fake accounts.
Damage to Consumer Trust:
Text spoofing can erode consumer trust in communication channels, making individuals more wary of the messages they receive. When recipients encounter frequent text spoofing, they may become skeptical of legitimate messages, hindering effective communication between businesses and customers.
Regulatory Measures:
Regulatory bodies and telecommunication authorities are increasingly implementing measures to combat text spoofing. These measures may include strengthening security protocols, imposing stricter regulations on message origin verification, or collaborating with service providers to prevent the misuse of text messaging services.
Conclusion
Text spoofing poses significant risks to individuals, businesses, and the overall trust in digital communication. Understanding the implications of text spoofing and taking necessary precautions is crucial in safeguarding privacy, security, and personal information.
By exercising caution, implementing security measures, staying informed, and promptly reporting suspicious activities, we can collectively combat text spoofing and protect ourselves from falling victim to malicious intents. It is essential to remain vigilant in the digital realm and foster a culture of cybersecurity to mitigate the risks associated with text spoofing.
Implement text message automation in your business operations.